Bruteforce/DFS/Backtracking Algorithm using Javascript to Solve
- Time:2020-09-07 12:13:31
- Class:Weblog
- Read:34
Use digit 1 to 8 only once and fill the below grid:
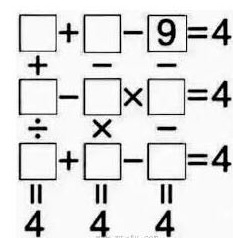
digit-grid
The arithmetic should proceed exactly from left to right and top to the bottom.
Bruteforce Algorithm to Solve the Numbers Grid Puzzle
The bruteforce algorithm should be a very trivial solution. There are 8 numbers to put in the 8 cell. Thus, the total solutions to check is 8! We can use 8 ugly nested loops and skip duplicates. The code nesting isn’t looking good, and is not flexible when the puzzle is later extended e.g. to a much bigger dimension 10×10 etc.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | for (let a = 1; a <= 8; ++ a) { let b = 13 - a; if (b >= 9) continue; if (b == a) continue; for (let c = 1; c <= 8; ++ c) { if ((c == a) || (c == b)) continue; for (let d = 1; d <= 8; ++ d) { if ((d == a) || (d == b) || (d == c)) continue; for (let e = 1; e <= 8; ++ e) { if ((e == a) || (e == b) || (e == c) || (e == d)) continue; if ((c - d) * e == 4) { for (let f = 1; f <= 8; ++ f) { if ((f == a) || (f == b) || (f == c) || (f == d) || (f == e)) continue; for (let g = 1; g <= 8; ++ g) { if ((g == a) || (g == b) || (g == c) || (g == d) || (g == e) || (g == f)) continue; for (let h = 1; h <= 8; ++ h) { if ((h == a) || (h == b) || (h == c) || (h == d) || (h == e) || (h == f) || (h == g)) continue; if ((a + c == 4 * f) && ((b - d) * g == 4) && (9 - e - h == 4)) { console.log(a, "+", b, "-", 9, "=4"); console.log(c, "-", d, "*", e, "=4"); console.log(f, "+", g, "-", h, "=4"); } } } } } } } } } |
for (let a = 1; a <= 8; ++ a) {
let b = 13 - a;
if (b >= 9) continue;
if (b == a) continue;
for (let c = 1; c <= 8; ++ c) {
if ((c == a) || (c == b)) continue;
for (let d = 1; d <= 8; ++ d) {
if ((d == a) || (d == b) || (d == c)) continue;
for (let e = 1; e <= 8; ++ e) {
if ((e == a) || (e == b) || (e == c) || (e == d)) continue;
if ((c - d) * e == 4) {
for (let f = 1; f <= 8; ++ f) {
if ((f == a) || (f == b) || (f == c) || (f == d) || (f == e)) continue;
for (let g = 1; g <= 8; ++ g) {
if ((g == a) || (g == b) || (g == c) || (g == d) || (g == e) || (g == f)) continue;
for (let h = 1; h <= 8; ++ h) {
if ((h == a) || (h == b) || (h == c) || (h == d) || (h == e) || (h == f) || (h == g)) continue;
if ((a + c == 4 * f) && ((b - d) * g == 4) && (9 - e - h == 4)) {
console.log(a, "+", b, "-", 9, "=4");
console.log(c, "-", d, "*", e, "=4");
console.log(f, "+", g, "-", h, "=4");
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}The only solution found by the above Javascript bruteforce code is:
5 + 8 - 9 =4 + - - 7 - 6 * 4 =4 / * - 3 + 2 - 1 =4 = = = 4 4 4
Another bruteforce algorithm would be to obtain the 8! permutation and then check the validity of each solution.
DFS with BackTracking Algorithm to Solve the Number Puzzle
A better approach would be to use Depth First Search Algorithm to backtracking the search tree – this allows us to abandon the search branches which can’t be solutions:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | (function dfs(sol) { if (sol.length == 9) { console.log(sol); return true; } if (sol.length == 2) { if (sol[0] + sol[1] - 9 != 4) return false; sol.push(9); // 9 is given //return dfs(sol); } for (let i = 1; i <= 8; ++ i) { if (!sol.includes(i)) { // can only use once if (sol.length == 5) { // second row if ((sol[3] - sol[4]) * i != 4) continue; } if (sol.length == 6) { // first column if ((sol[0] + sol[3]) / i != 4) continue; } if (sol.length == 7) { // second column if ((sol[1] - sol[4]) * i != 4) continue; } if (sol.length == 8) { // third row if (sol[6] + sol[7] - i != 4) continue; // third column if (sol[2] - sol[5] - i != 4) continue; } sol.push(i); if (dfs(sol)) { return true; } sol.pop(); } } return false; })([]); |
(function dfs(sol) {
if (sol.length == 9) {
console.log(sol);
return true;
}
if (sol.length == 2) {
if (sol[0] + sol[1] - 9 != 4) return false;
sol.push(9); // 9 is given
//return dfs(sol);
}
for (let i = 1; i <= 8; ++ i) {
if (!sol.includes(i)) { // can only use once
if (sol.length == 5) {
// second row
if ((sol[3] - sol[4]) * i != 4) continue;
}
if (sol.length == 6) {
// first column
if ((sol[0] + sol[3]) / i != 4) continue;
}
if (sol.length == 7) {
// second column
if ((sol[1] - sol[4]) * i != 4) continue;
}
if (sol.length == 8) {
// third row
if (sol[6] + sol[7] - i != 4) continue;
// third column
if (sol[2] - sol[5] - i != 4) continue;
}
sol.push(i);
if (dfs(sol)) {
return true;
}
sol.pop();
}
}
return false;
})([]);Running the above Javascript DFS code prints the 8 numbers that is the correct solution:
1 2 3 4 | [ 5, 8, 9, 7, 6, 4, 3, 2, 1 ] |
[ 5, 8, 9, 7, 6, 4, 3, 2, 1 ]
The solution is superior to the above bruteforce approach. This can also be solved via Breadth First Search Algorithm.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
Recommend:How to Convert Integer to the Sum of Two No-Zero Integers?
Algorithm to Generate the Spiral Matrix in Clock-wise Order
How to Remove the Duplicates from Sorted List (Leaving Only Dist
How to Sort a Linked List by Converting to Array/Vector?
Know The Effective and Smart SEO Reporting Tool You Must Use
Pro Content Marketing Tips You Can Implement NOW
8 WordPress Plugins for Better User Experience
6 Eye-Opening Tips for Measuring and Improving the Impact of You
Should a Professional Blog Be Funny?
How to Perform a Meaningful Content Audit of Your Blog Section
- Comment list
-
- Comment add