How to Delete N Nodes After M Nodes of a Linked List?
- Time:2020-09-08 11:19:41
- Class:Weblog
- Read:30
Given the head of a linked list and two integers m and n. Traverse the linked list and remove some nodes in the following way:
Start with the head as the current node.
Keep the first m nodes starting with the current node.
Remove the next n nodes
Keep repeating steps 2 and 3 until you reach the end of the list.
Return the head of the modified list after removing the mentioned nodes.Follow up question: How can you solve this problem by modifying the list in-place?
delete-n-nodes-after-m-nodes-of-a-linked-list
Example 1:
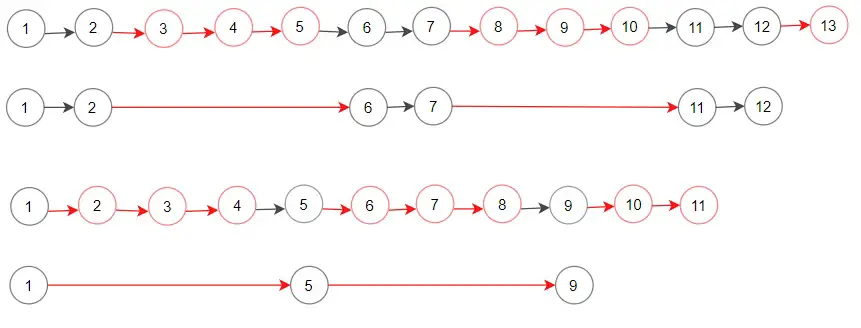
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13], m = 2, n = 3
Output: [1,2,6,7,11,12]
Explanation: Keep the first (m = 2) nodes starting from the head of the linked List (1 ->2) show in black nodes.
Delete the next (n = 3) nodes (3 -> 4 -> 5) show in read nodes.
Continue with the same procedure until reaching the tail of the Linked List.
Head of linked list after removing nodes is returned.Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11], m = 1, n = 3
Output: [1,5,9]
Explanation: Head of linked list after removing nodes is returned.Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11], m = 3, n = 1
Output: [1,2,3,5,6,7,9,10,11]Example 4:
Input: head = [9,3,7,7,9,10,8,2], m = 1, n = 2
Output: [9,7,8]Constraints:
The given linked list will contain between 1 and 10^4 nodes.
The value of each node in the linked list will be in the range [1, 10^6].
1 <= m,n <= 1000Hints:
Traverse the Linked List, each time you need to delete the next n nodes connect the nodes previous deleting with the next node after deleting.
C++ Algorithm to Delete N Nodes After M Nodes of a Linked List in Place
Most linked list problems can be helped by using a dummy header pointer. In this particular problem, we need also a previous pointer. By skipping current M nodes, and we need to link the previous pointer to next pointer – which basically delete N nodes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* deleteNodes(ListNode* head, int m, int n) { ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1); ListNode* prev = dummy; prev->next = head; while (head != NULL) { for (int i = 0; (i < m) && (head != NULL); ++ i) { prev = head; head = head->next; } for (int i = 0; (i < n) && (head != NULL); ++ i) { head = head->next; } prev->next = head; } return dummy->next; } }; |
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteNodes(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* prev = dummy;
prev->next = head;
while (head != NULL) {
for (int i = 0; (i < m) && (head != NULL); ++ i) {
prev = head;
head = head->next;
}
for (int i = 0; (i < n) && (head != NULL); ++ i) {
head = head->next;
}
prev->next = head;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};We also need to take care of the cases when there are less than M nodes to skip. In this case, we would just point previous pointer to NULL.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
Recommend:How to Avoid Paying Too Much Fee when Cashing out Bitcoin via Wi
The Common Kodi Errors and Use of Free VPN for Linux
Java Pattern: Use Atomic Boolean to Return Single Usage Object
Significance of HTML and CSS in Mobile App Development
How to Reverse Words in a String using Modern Programming Langua
The Python Function to Retrieve the Producer Reward for Witness
Function to Compute the Average Salary Excluding the Minimum and
Efficient Algorithms to Compute The kth Factor of a Natural Numb
Can We Make Arithmetic Progression From Sequence of Numbers?
How to SSH to Remote Host using the Priviate/Public Keys Authent
- Comment list
-
- Comment add