Linear Algorithm to Check If All 1’s Are at Least Length K
- Time:2020-09-09 14:04:20
- Class:Weblog
- Read:37
Given an array nums of 0s and 1s and an integer k, return True if all 1’s are at least k places away from each other, otherwise return False.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1], k = 2
Output: true
Explanation: Each of the 1s are at least 2 places away from each other.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,0,0,1,0,1], k = 2
Output: false
Explanation: The second 1 and third 1 are only one apart from each other.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1], k = 0
Output: trueExample 4:
Input: nums = [0,1,0,1], k = 1
Output: trueConstraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
0 <= k <= nums.length
nums[i] is 0 or 1Hints:
Each time you find a number 1, check whether or not it is K or more places away from the next one. If it’s not, return false.
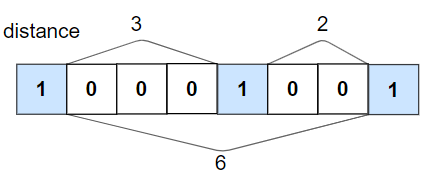
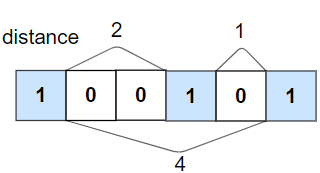
Check If All 1’s Are at Least Length K Places Away
We remember and update the last position of the 1’s if we go through the binary array one by one. And return false if we found current is one and the distance is more than K places away than the last one. If it reaches the end, then we simply return true.
The complexity is O(N) linear as we are iterating the array once.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | class Solution { public: bool kLengthApart(vector<int>& nums, int k) { int last = -1; for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++ i) { if (nums[i] == 1) { if (last != -1) { if (i - last - 1 < k) return false; } last = i; } } return true; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
bool kLengthApart(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int last = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++ i) {
if (nums[i] == 1) {
if (last != -1) {
if (i - last - 1 < k) return false;
}
last = i;
}
}
return true;
}
};Note that we may not need to check if the flag is negative (which is intialised to negative one). Instead, we can initialise the last position to (-k-1).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | class Solution { public: bool kLengthApart(vector<int>& nums, int k) { int last = -k - 1; for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++ i) { if (nums[i] == 1) { if (i - last - 1 < k) return false; last = i; } } return true; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
bool kLengthApart(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int last = -k - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++ i) {
if (nums[i] == 1) {
if (i - last - 1 < k) return false;
last = i;
}
}
return true;
}
};This is a much cleaner implementation of the same algorithm.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
Recommend:2020 Design Trends [Infographic]
8 Content Marketing Plugins You Need For Your WordPress Blog
Tips to Make Money from the Comfort of Your Own Home
5 Tips for Protecting Your Freelance Business from Liabilities
5 Easy Ways On How To Build An Authority Website
How to Protect Your WordPress Site From Hackers
Top 10 Relationship Blogs With the Best Pieces of Advice in 2020
How to Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal in P
Dynamic Programming Algorithm to Compute the Block Sum in a Matr
Smallest Multiple Algorithm using Bruteforce or GCD/LCM
- Comment list
-
- Comment add